How Two Currency Systems Are Evolving for Different Generations
September 14, 2024

Forex Indonesia: In Indonesia today, the term Forex Indonesia carries a broader meaning than ever before. On one side are fast-growing digital platforms where young traders speculate on global currency values. On the other, physical money changers continue to serve local communities with direct, over-the-counter services. Both are part of the same ecosystem — yet they serve distinctly different generations, behaviors, and economic purposes.
What was once a simple question of “where to change money” has now evolved into a larger discussion about financial access, digital behavior, and how people choose to interact with global currency flows.
Why Forex Trading Appeals to the Digitally Literate
The digital trading boom in Indonesia didn’t happen overnight. With the rise of fintech and mobile banking, younger Indonesians are increasingly drawn to forex trading as an entry point into the world of personal finance. Platforms licensed by BAPPEBTI now offer retail traders access to real-time market data, technical analysis tools, and international currency pairs — all from the convenience of a mobile phone.
The flexibility of forex trading is part of its appeal. It can be done anytime during weekdays, it offers high liquidity, and the potential returns — while not guaranteed — are attractive to risk-tolerant investors. But this accessibility also comes with pitfalls. The volatility of the forex market makes it a high-risk environment, especially for newcomers who may not fully understand how leverage or spreads affect outcomes.
Still, the trend shows no signs of slowing. In major cities like Jakarta, Bandung, and Yogyakarta, forex trading has become a popular topic among university students, tech workers, and side-hustlers looking to grow their savings outside conventional banking.
Why Money Changers Remain Unshaken in Daily Transactions

Source: crowncurrency
At the same time, brick-and-mortar money changers remain a constant in Indonesian daily life. Tourists, business travelers, and overseas-bound students still rely on licensed money changers for their currency needs. Whether it’s USD, EUR, SGD, or JPY, physical outlets offer convenience, clarity, and immediate access to foreign banknotes.
These services are especially important in cities with international travel hubs and migrant worker populations. Regulated by Bank Indonesia, money changers are required to post exchange rates publicly and issue official receipts. That level of transparency, combined with a straightforward transaction process, continues to build trust — especially among older users and less digitally inclined communities.
Money changers may lack the thrill of fast-paced trading apps, but they offer peace of mind. You know exactly how much you’re getting, without hidden fees or speculative pressure. In this version of Forex Indonesia, practicality still leads.
Diverging Functions, Not Just Formats
Source: Adaremit
What’s most striking about the evolution of Forex Indonesia is that these two services — forex trading and money exchange — aren’t replacing each other. Instead, they are diverging further, each becoming more specialized in its role.
Forex trading is now primarily associated with financial strategy, investment thinking, and speculative behavior. The goal is not to get currency for spending, but to profit from movements in its value. It’s a time-driven, screen-based experience that thrives on market information and fast execution.
In contrast, money changers are embedded in the physical economy. Their role is functional and transactional. Customers approach with a purpose — to exchange money for a trip, a tuition payment, or a remittance. They are not chasing profit but fulfilling a need.
These different value systems show how Indonesia’s currency market is becoming more segmented — and more adaptive to user expectations.
Forex Indonesia: Behavior, Trust, and Familiarity Drive Choice
User behavior tells the clearest story. A mid-career worker with financial ambitions may explore forex trading on weekends, experimenting with small trades and technical indicators. Meanwhile, a parent preparing for a family trip to Singapore might head to a well-known money changer at the mall. Both are engaging with foreign currency — just in radically different ways.
Trust also plays a role. While younger users are increasingly confident in digital platforms, older generations tend to stick with what’s tangible and verified. Bank Indonesia’s licensing system reinforces this by ensuring every money changer displays credentials and issues receipts. Likewise, BAPPEBTI’s broker registry helps online users avoid scams and unregulated platforms.
As digital literacy spreads and financial tools become more personalized, we may see more crossover between the two services. But for now, behavior remains distinct.
Forex Indonesia: Rates Reflect Purpose, Not Just Math
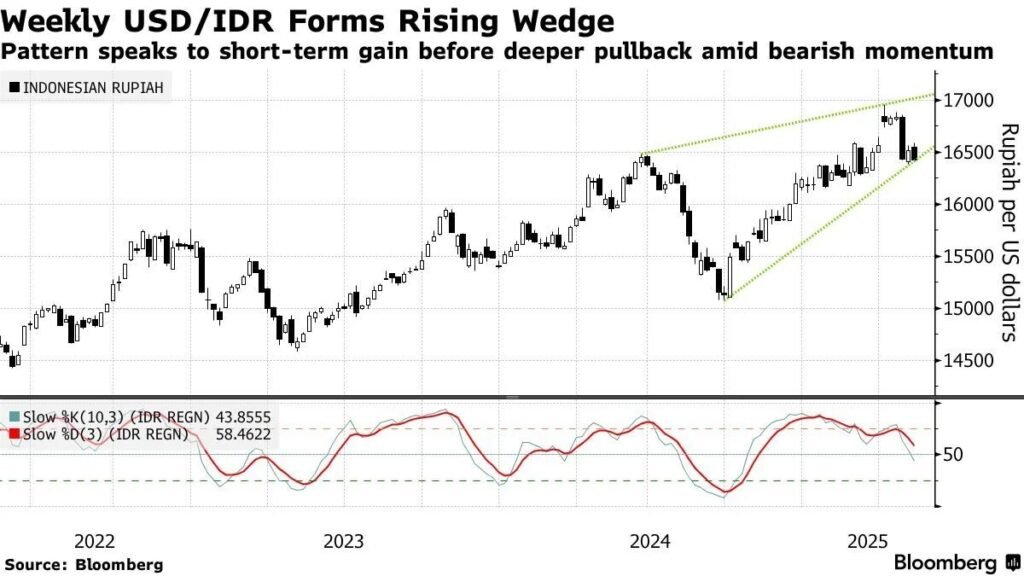
Source: Bloomberg
Rates offered by traders and money changers often differ — not because of accuracy, but because of what each service is designed to do. Forex trading platforms offer interbank rates with narrow spreads, appealing to those seeking precision and speed. However, these come with execution risks and sometimes added costs, such as swap fees or commissions.
Money changers, on the other hand, build their margin into the posted rate. While slightly less favorable, the rate is guaranteed at the moment of exchange — with no risk of slippage. For the customer, the rate reflects reliability, not a bet on market timing. That’s an important distinction in how users evaluate value in the Forex Indonesia marketplace.
Forex Indonesia: Regulation Keeps Both Systems in Check

Source: The Malaysian Resource
Whether digital or physical, legitimacy matters. In recent years, Indonesia has tightened regulations on forex activity, cracking down on illegal brokers and unauthorized exchange points. BAPPEBTI ensures forex trading platforms operate transparently, while Bank Indonesia enforces compliance among money changers.
This dual oversight not only protects consumers but helps maintain public confidence. In a landscape where scams are still a threat — especially on social media — clarity and licensing provide an anchor. For the Forex Indonesia ecosystem to thrive, both services need to stay within visible legal boundaries.
Final Thought: Coexistence, Not Competition
Ultimately, forex trading and money changing are not in competition — they’re serving different needs, different mindsets, and different moments. One is a calculated risk taken with digital tools and real-time data. The other is a face-to-face exchange designed for reliability and speed.
The fact that both are growing suggests a healthy, responsive financial market. As more Indonesians become financially literate, we may see more nuanced uses of each — but the separation in purpose is likely to remain. For now, Forex Indonesia is best understood as two systems moving forward on parallel paths.

